What is a Cochlear Implant?
According to the National Institute of Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIDCD):
A cochlear implant is a small, complex electronic device that can help to provide a sense of sound to a person who is profoundly deaf or severely hard-of-hearing. The implant consists of an external portion that sits behind the ear and a second portion that is surgically placed under the skin.
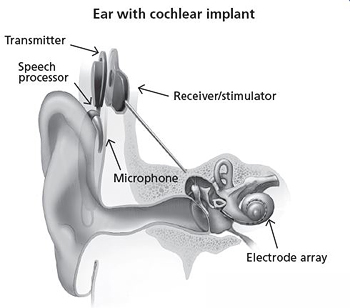
An implant has the following parts:
- A microphone, which detects sound from the environment
- A speech processor, which selects and arranges sounds picked up by the microphone.
- A transmitter and receiver/stimulator, which receives signals from the speech processor and convert them into electric impulses.
- An electrode array, which is a group of electrodes that deliver the signals from the stimulator and sends them to different, frequency-specific regions along the auditory nerve.
- A cochlear implant does not restore normal hearing. Instead, it can give a deaf person a useful representation of sounds in the environment and help him or her to understand speech.
